7 Steps to Combining Design Thinking with OKRs
Design Thinking and OKRs (Objectives and Key Results) are both popular approaches to problem solving and goal setting. Design thinking is a human-centered, iterative approach to problem solving that seeks to understand user needs and develop solutions that meet those needs. OKRs, on the other hand, is a goal-setting framework that involves defining specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound objectives along with key results to track progress towards those objectives.
Combining these two approaches can lead to a more effective and holistic approach to problem solving and goal setting. Design thinking can inform the creation of user centred OKRs, while OKRs can provide a clear roadmap for implementing and measuring the impact of design thinking solutions. This combination can help to ensure that the solutions developed through design thinking are aligned with organizational goals and that progress towards those goals is continuously monitored and evaluated.
For example, an organization could use design thinking to understand the needs of its customers and develop a new product that meets those needs. The OKRs for the project could then be developed to ensure that the product is delivered on time, within budget, and meets the desired customer requirements. Key results could include metrics such as customer satisfaction, adoption rates, and revenue generated.
Steps in Combining Design Thinking with OKRs
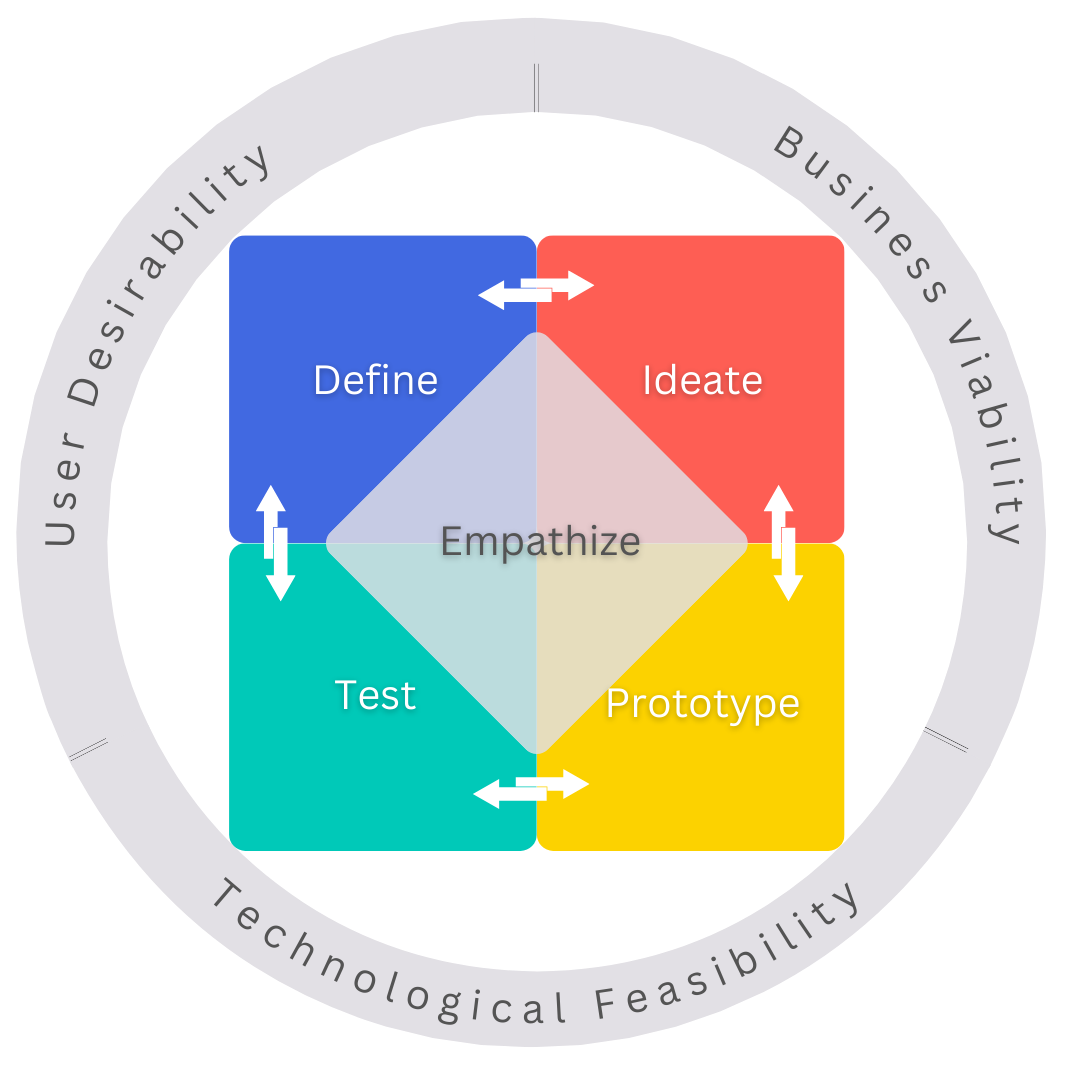
Combining OKRs (Objectives and Key Results) with design thinking can help organizations to achieve their goals in a more creative and user-centered way. Here are some steps to combining OKRs with design thinking:
- Start with User Research: Use design thinking techniques such as empathy maps and customer journey maps to understand the needs and wants of the users who are affected by the problem you are trying to solve.
- Define the Problem: Use design thinking to define the problem in a way that is specific, actionable, and tied to the needs and wants of the users.
- Set Aspirational Objectives: Use OKRs to set aspirational objectives that are tied to the problem you have defined. Seek to wordsmith the Objective in ways that improve your customer’s life and excite your team at the same time.
- Develop Key Results: Let the objective drive the key results that will help to track progress. Remember it’s the collection of Key Results working together that will help you achieve your objective.
- Ideate for Initiatives: Get creative with potential solutions. These are your possible initiatives that will be generated using techniques like brainstorming, reverse brainstorming, mid-mapping, etc. Use tools like PICK Chart to prune down those initiatives worthy of prototyping.
- Prototype and Test: Use design thinking to prototype and test potential solutions to the problem. This can involve creating prototypes, conducting user testing, and iterating based on feedback.
- Refine, Review, Repeat: Use OKRs and design thinking to refine and repeat the process until a solution is found that meets the needs and wants of the users and achieves the objectives. Use OKRs to track progress towards the objectives and key results and use design thinking to continuously gather feedback and iterate on the solution.
Example: Combining Design Thinking with OKRs
Here is an example of how OKRs and design thinking can be combined in a real-world scenario:
Problem: A company wants to improve customer satisfaction with its online shopping platform.
Step 1: Start with User Research
The company uses design thinking techniques to gather customer feedback and understand their needs and wants. This includes conducting customer surveys, focus groups, and online research.
Step 2: Define the Problem
Based on the user research, the company identifies that customers are frustrated with the checkout process on the online shopping platform. The problem is defined as: “To improve customer satisfaction by streamlining the checkout process on the online shopping platform.”
Step 3: Set Aspirational Objectives:
Objective: Improve customer satisfaction by streamlining the checkout process on the online shopping platform
Step 4: Develop Key Results
KR 1: Reduce the number of clicks needed to complete a checkout by 50%
KR 2: Increase the percentage of customers who complete a purchase by 15%
KR 3: Decrease customer abandonment rate by 10%
Step 5: Ideate for Initiatives
For KR 1: Reduce the number of clicks needed to complete a checkout by 50%, imagine the team comes up with 5 possible solutions.
- Simplify the Form: Reduce the number of fields required during checkout, only asking for the information that is absolutely necessary. For example, consider using pre-populated fields where possible or offering a guest checkout option.
- Use Progressive Disclosure: Progressive disclosure involves only showing additional information or options when the customer needs them. For example, only asking for shipping information after the customer has entered their billing information.
- Implement One-Click Checkout: Offer a one-click checkout option that allows customers to complete a purchase with a single click, eliminating the need to go through multiple steps.
- Autofill Information: Implement an autofill feature that fills in the customer’s information for them based on previous purchases or saved information.
- Mobile Optimization: Ensure that the checkout process is optimized for mobile devices, with a clear and concise design that is easy to navigate.
At this stage, you can run some analysis to come up with one or two of these potential initiatives that will enter the Prototype funnel. You may run a similar exercise for the other two Key Results.
Step 6: Prototype and Test:
The company uses design thinking to prototype potential solutions to the problem, such as reducing the number of fields required during checkout and offering one-click checkout. The prototypes are tested with customers to gather feedback and validate the solution.
Step 7: Refine, Review, Repeat
Based on the customer feedback, the company iterates on the solution, refining and adjusting it until the solution meets the needs and wants of the users and achieves the objectives. Using OKRs, the team tracks progress towards the objectives and key results, monitoring metrics such as the number of clicks needed to complete a checkout, the percentage of customers who complete a purchase, and the customer abandonment rate.
In this example, the company used OKRs and design thinking to align their goal of improving customer satisfaction with the needs and wants of their customers. The combination of the two approaches helped the company to take a user-centered and iterative approach to solving the problem, which led to a more effective solution that was better aligned with the company’s goals.
Summary
In conclusion, combining design thinking and OKRs can lead to a more effective approach to problem solving and goal setting that is centred around the needs of users and aligned with organizational goals.
By combining OKRs with design thinking, organizations can ensure that their goals are aligned with the needs and wants of their users, and that they are taking a creative and iterative approach to solving problems. This can lead to more effective and user-centered solutions that are better aligned with organizational goals and vision.